The principle of hydraulic cavitation phenomenon and its application in wastewater treatment
1. Cavitation phenomenon
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the pressure in a liquid is compressed to a low enough critical pressure by an external force, and cavities are formed inside the liquid, which are filled with steam and dissolved gases in the liquid. Under violent compression, these vapor - and gas-filled cavities implode, creating enormous implosive forces that trigger local hot spots and release large amounts of energy. The temperature can be as high as 500-15000K, and the pressure range is 100-5000 atmospheres.
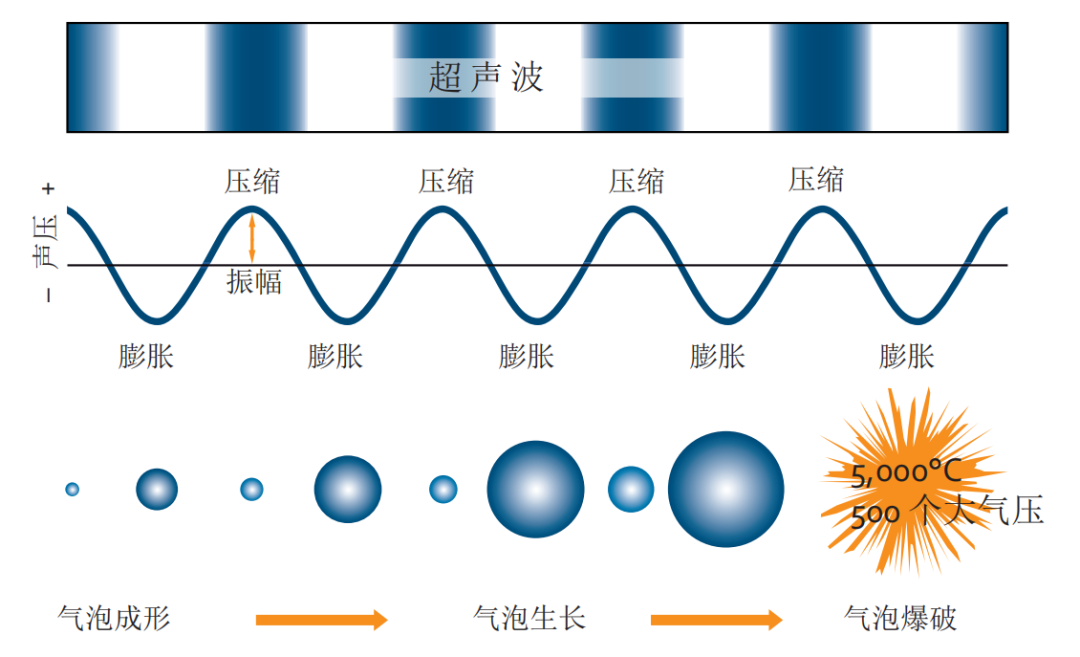
Ultrasonic cavitation diagram
In the process of cavitation, in addition to high temperature and high pressure, it also causes a lot of physical and chemical changes. Under extreme cavitation conditions, water molecules can decompose into a variety of species with high oxidation potential, including hydroxyl radicals (·OH), ·OOH, H2O2, etc., which react with organic compounds contained in sewage. At the same time, the huge implosion force and shear force generated by the collapse of cavitation bubbles can destroy the molecular bonds of organic pollutants or make them thermal decomposition, and destroy the cell wall of microorganisms, so as to achieve the purpose of degrading macromolecular organic matter and destroying microorganisms in sewage. In addition, the microjets, local turbulence and microcirculation generated by cavitation bubble collapse enhance the gas-liquid mass transfer of reactants and reduce the mass transfer resistance of the system.
Therefore, cavitation is regarded as an effective and promising technology, which is widely used in disinfection, cell fragmentation, sludge treatment, organic degradation and other fields. The combination of other technologies in sewage treatment can achieve the purpose of reducing chemicals, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
2. Hydraulic cavitation
According to the different ways of cavitation, it can be divided into four types: photocavitation, ionic cavitation, acoustic cavitation and hydraulic cavitation. Compared with other cavitation technologies, hydraulic cavitation has the characteristics of large operation scale, good energy saving effect and simple equipment, so it is a very potential wastewater treatment technology.
Usually, hydraulic cavitation is generated by the change of liquid flow and pressure. Throttle valve is used to reduce the cross section of fluid channel, and the increase of velocity and kinetic energy is obtained through the reduction of pressure. At the same time, boundary layer separation and turbulence occur. The cavitation begins when the local pressure drops below the cavitation threshold pressure.

However, when the pressure recovers or rises above the cavitation threshold, the cavity collapses and the microjet produces turbulence downstream of the liquid contraction. This change can be triggered by a device with a specific structure, and the structure and type of different devices are different, but all of them mainly play the role of throttle valves. Hydraulic cavitation units are generally divided into five types, namely venturi, orifice, rotary, turbine-based, and other types.
3, hydraulic cavitation and ozone catalytic technology
Compared with the use of hydraulic cavitation alone, the collaborative technology based on hydraulic cavitation has better degradation efficiency. The use of hydraulic cavitation in combination with other advanced oxidation technologies can not only promote the degradation of pollutant molecules, but also reduce the treatment time and the amount of oxidants. Among them, ozone catalytic oxidation has attracted wide attention in the field of global environmental governance due to its advantages of non-selectivity and environmental friendliness.
Ozone, with an oxidation potential of 2.07eV, takes air or oxygen as a gas source and is produced by an ozone generator, which has strong oxidation properties in alkaline solutions. However, the ozone reaction alone is only effective for organic compounds with specific functional groups such as aromatic rings and unsaturated hydrocarbons, and not for substances such as saturated hydrocarbons, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. In addition, ozone is easily decomposed into oxygen before it is dissolved into the solution, and plays an effective role in oxidation.
The combined process of hydraulic cavitation and ozone shows a good synergistic effect. Under the condition of hydraulic cavitation, ozone can decompose into ·OH (2.8eV) with high oxidation potential, and the oxidation effect is second only to fluorine (3.0eV). On the one hand, the combined system can significantly improve the removal efficiency of pollutants with less ozone. On the other hand, this operation process does not produce by-products and cause secondary pollution. Reduce operating costs while saving energy.

Application case of advanced ozone oxidation device combined with hydraulic cavitation technology
CDOF(Cyclonic Dissolved Ozone Flotation unit) developed by Keli Technology creatively combines advanced ozone oxidation technology, cavitation supercritical catalysis, swirl technology and dissolved gas flotation technology to achieve efficient and comprehensive removal of all kinds of difficult wastewater. Good application results have been obtained in many sewage treatment projects.
